 |
For more information call
The Wellington Hospital: 020 7483 5589
Fortius Clinic: 0845 853 1000 The Yorkshire Clinic: 01274 621600 |
Hip Arthroscopy Procedures - General Principles
Hip arthroscopy is the term used for keyhole surgery of the hip. It is a surgical procedure that has been around over the past twenty years, but has only recently gained popularity due to advancement in surgical techniques and a wider understanding of hip pathology. Whereas in the past options were limited for patients with hip problems and in some cases, hip replacement was inevitable, it is now recognised that hip arthroscopy can potentially postpone the need for hip replacement.
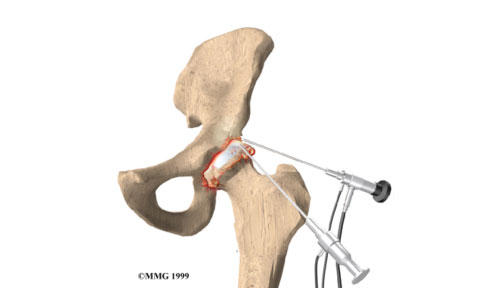
Hip arthroscopy is a minimally-invasive procedure used to evaluate and treat certain disorders of the hip. It is the alternative to open surgery where longer recovery periods are expected with an increased risk of infection and morbidity in older patients.
Hip arthroscopy at the Yorkshire Clinic and The Wellington Hospital is performed by Professor the Ernest Schilders, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, who has a special interest in groin and sports injuries, and arthroscopic surgery of the hip. Ernest Schilders trained and qualified in Antwerp, Belgium, and has gained an international reputation through his treatment of high-profile, professional athletes, his research activities and publishing of articles. He is a renowned guest-speaker at international sports and medical conferences.
Hip Arthroscopy - What does the procedure involve?
Hip arthroscopy is currently performed on an in-patient basis under general anaesthetic. Small incisions are made in the patient’s hip area and a camera lens is inserted through these holes so that the surgeon may visualise the inside of the patient's hip joint. The visible area of the hip consists of two compartments: a central and a peripheral compartment. The central compartment is the area of the hip that contains cartilage and is the space between the ball and socket. Cartilage lesions and labral tears in this compartment can be visualised and treated. The peripheral compartment is the area of the femoral neck and the hip capsule. Bumps or so-called CAM deformities of the femoral neck can be removed. Labral tears can be treated with a resection of the tear or repair depending on the type of tear.